异步编程利器CompletableFuture
异步编程利器CompletableFuture
一、简介
FutureTask的get()方法在Future计算完成之前会一直处于阻塞状态下,isDone()方法容易耗费CPU资源,对于真正的异步处理我们是希望能通过传入回调函数,在Future结束时自动调用该回调函数,这样,我们就不用等待结果。阻塞的方式和异步编程的设计理念相违背,而轮询的方式也会耗费CPU资源。因此JDK8中出现了一种新的工具类:CompletableFuture。
CompletableFuture是FutureTask的增强版,提供的是一种类似观察者模式的机制,可以让任务执行完成后通知监听的一方。在任务执行完成之前,监听方可以去干别的事情。
在Java8中,CompletableFuture提供了非常强大的Future的扩展功能,可以帮助我们简化异步编程的复杂性,并且提供了函数式编程的能力,可以通过回调的方式处理计算结果,也提供了转换和组合CompletableFuture的方法。它能代表一个明确完成的Future,也有可能代表一个完成阶段(CompletableStage)。它支持在计算完成后触发一些函数或者执行某些动作。它实现了Future和CompletionStage接口。
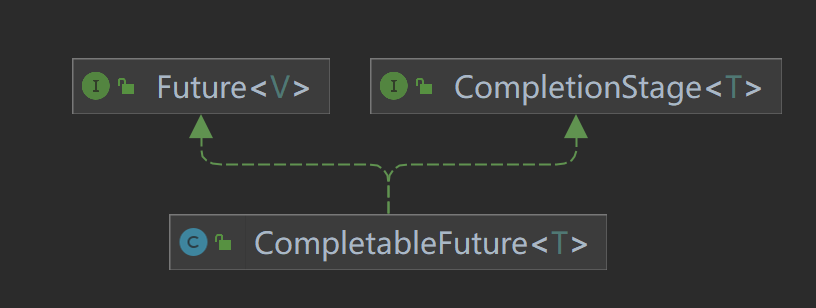
CompletionStage代表异步计算过程中的某一个阶段,一个阶段完成以后可能会触发另外一个阶段。
一个阶段的计算可以是一个Function,Consumer或者Runnable,比如:stage.thenApply(x -> square(x)).thenAccept(x -> System.out.print(x)).thenRun(() -> System.out.println());
一个阶段的执行可能是被单个阶段的完成触发,也可能是由多个阶段一起触发
二、四大静态方法入门
java不推荐使用构造方法构造CompletableFuture,推荐使用下面的四大静态方法。
1、runAsync无返回值(默认线程池)
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable);2、runAsync无返回值(自定义线程池)
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable,Executor executor);3、supplyAsync有返回值(默认线程池)
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier);4、supplyAsync有返回值(自定义线程池)
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier,Executor executor);5、源码测试
package com.gyd;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class CompletableFutureDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
System.out.println("======CompletableFuture.runAsync的演示(无返回值,默认线程池)");
runAsync1();
System.out.println("======CompletableFuture.runAsync的演示(无返回值,自定义线程池)");
runAsync2();
System.out.println("======CompletableFuture.supplyAsync1的演示(有返回值,默认线程池)");
supplyAsync1();
System.out.println("======CompletableFuture.supplyAsync1的演示(有返回值,自定义线程池)");
supplyAsync2();
}
public static void runAsync1() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//不推荐
//CompletableFuture completableFuture = new CompletableFuture();
CompletableFuture<Void> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);}catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}
});
System.out.println(completableFuture.get());
}
public static void runAsync2() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
CompletableFuture<Void> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);}catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}
},executorService);
System.out.println(completableFuture.get());
executorService.shutdown();
}
public static void supplyAsync1() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);}catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}
return "Hello Supply";
});
System.out.println(completableFuture.get());
}
public static void supplyAsync2() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);}catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}
return "Hello Supply";
},executorService);
System.out.println(completableFuture.get());
executorService.shutdown();
}
}输出结果:
======CompletableFuture.runAsync的演示(无返回值,默认线程池)
ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-25
null
======CompletableFuture.runAsync的演示(无返回值,自定义线程池)
pool-1-thread-1
null
======CompletableFuture.supplyAsync1的演示(有返回值,默认线程池)
ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-25
Hello Supply
======CompletableFuture.supplyAsync1的演示(有返回值,自定义线程池)
pool-2-thread-1
Hello Supply
Process finished with exit code 0三、常用方法
1、获得结果和触发计算
package com.gyd;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;
public class CompletableFutureDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException {
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->{
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return "abc";
});
//不见不散
// System.out.println(completableFuture.get());
//过时不候(抛出TimeoutException)
// System.out.println(completableFuture.get(2,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
//立即返回(立即获取结果不阻塞,没有计算完成的情况 给一个默认值)
// System.out.println(completableFuture.getNow("xxx"));
//complete方法用于判断是否执行完成,未执行完成则返回默认值,注意该方法只能被执行一次
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4);
System.out.println(completableFuture.complete("completeValue")+" "+completableFuture.join());
}
}2、对计算结果进行处理
thenApply:计算结果存在依赖,不同步骤的线程执行串行化,若某个步骤发生异常,则不进入下一步骤并直接进入异常处理流程。
package com.gyd;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class CompletableFutureDemo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->{
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("111");
return 1;
},executorService).thenApply(f ->{
System.out.println("222");
//若当前步骤有异常,则不会继续执行后续步骤,直接进入异常处理流程exceptionally
return f+2;
}).thenApply(f->{
System.out.println("333");
return f+3;
}).whenComplete((v,e) ->{
if (e == null) System.out.println("v: "+v);
}).exceptionally( e ->{
//发生异常时的处理
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("发生异常");
return null;
});
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"先去忙别的事情");
}
}handle:计算结果存在依赖,不同步骤的线程执行串行化,若某个步骤发生异常,携带异常信息继续执行下一步骤。
package com.gyd;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class CompletableFutureDemo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->{
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("111");
return 1;
},executorService).handle((f,e) ->{
System.out.println("222");
//若当前步骤有异常,则携带异常信息继续执行后续步骤
int i = 10/0;
return f+2;
}).handle((f,e)->{
System.out.println("上一步骤异常信息:"+e);
System.out.println("333");
return f+3;
}).whenComplete((v,e) ->{
if (e == null) System.out.println("v: "+v);
}).exceptionally( e ->{
//发生异常时的处理
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("发生异常");
return null;
});
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"先去忙别的事情");
}
}3、对计算结果进行消费
thenAccept: 任务A执行完继续执行任务B,任务B需要依赖任务A的计算结果,但任务B无返回值
package com.gyd;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class CompletableFutureDemo7 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->{
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("111");
return 1;
},executorService).thenApply(f ->{
System.out.println("222");
return f+2;
}).thenApply(f->{
return f+3;
}).thenAccept(f -> {
//接受任务的计算结果,进行消费处理,无返回结果
System.out.println("完成前两个步骤的任务,消费结果="+f);
});
executorService.shutdown();
}
}thenRun: 任务A执行完继续执行任务B,任务B不需要任务A的计算结果
package com.gyd;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class CompletableFutureDemo8 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->{
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("111");
return 1;
},executorService).thenApply(f ->{
System.out.println("222");
return f+2;
}).thenApply(f->{
return f+3;
}).thenRun(() ->{
System.out.println("执行完前两个步骤后,继续执行当前步骤");
});
executorService.shutdown();
}
}4、比较哪个步骤的任务执行快
applyToEither: 可以用来选出执行速度快的步骤。
package com.gyd;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class CompletableFutureDemo10 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException {
CompletableFuture<String> playA = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->{
try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
return "playA";
});
CompletableFuture<String> playB = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->{
try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
return "playB";
});
CompletableFuture<String> winer = playA.applyToEither(playB,f -> f+" is winer");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"-----:" + winer.join());
}
}5、对多个步骤的任务结果进行合并输出
thenCombine: 等待多个CompletionStage任务都完成后,最终把多个任务的结果合并处理输出。
示例将两个CompletionStage结果进行合并输出:
package com.gyd;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;
public class CompletableFutureDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException {
CompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->{
try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
return "task1";
});
CompletableFuture<String> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->{
try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
return "task2";
});
CompletableFuture<String> future3 = future1.thenCombine(future2, (x , y) -> {
return "合并:"+x+y;
});
System.out.println(future3.join());
}
}6、等待多个并行任务执行完成后返回
比如需要获取完整订单数据,可能需要填充订单的付款信息、地址信息、商品信息,这三部分数据都来自不同系统,互相没有依赖,可以并行获取。
package com.gyd;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class CompletableFutureDemo12 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException {
Map<String,Object> orderMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
CompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->{
try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
System.out.println("获取地址信息...");
orderMap.put("address","湖南");
return "task1";
});
CompletableFuture<String> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->{
try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
System.out.println("获取支付信息...");
orderMap.put("payinfo","10元");
return "task2";
});
CompletableFuture<String> future3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->{
try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
System.out.println("获取商品信息...");
orderMap.put("goods","袜子");
return "task3";
});
CompletableFuture<Void> result = CompletableFuture.allOf(future1,future2,future3);
result.join();
System.out.println("完整的订单数据:"+orderMap.toString());
}
}四、线程池的运行选择
废话少说,直接上代码:
package com.gyd;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class CompletableFutureDemo9 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException {
//a.模拟任务执行速度快的情况,系统底层会使用main线程处理任务
//运行结果:
//1号任务 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-25
//2号任务 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-25
//3号任务 main
//4号任务 main
System.out.println("===模拟任务执行速度快的情况,系统底层会使用main线程处理任务====");
test0();
//b.使用内置默认线程池+thenRun执行任务
//运行结果:
//1号任务 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-25
//2号任务 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-25
//3号任务 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-25
//4号任务 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-25
//null
System.out.println("===使用内置默认线程池+thenRun执行任务====");
test1();
//c.使用自定义线程池+thenRun执行任务
//运行结果:
//1号任务 pool-1-thread-1
//2号任务 pool-1-thread-1
//3号任务 pool-1-thread-1
//4号任务 pool-1-thread-1
System.out.println("===使用自定义线程池+thenRun执行任务====");
test2();
//d.使用内置默认线程池+thenRunAsync执行任务
//运行结果:
//1号任务 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-25
//2号任务 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-25
//3号任务 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-25
//4号任务 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-25
System.out.println("===使用内置默认线程池+thenRunAsync执行任务====");
test3();
//e.使用自定义线程池+thenRunAsync执行任务
//运行结果:
//1号任务 pool-2-thread-1
//2号任务 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-25
//3号任务 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-25
//4号任务 ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-25
System.out.println("===使用自定义线程池+thenRunAsync执行任务====");
test4();
}
//a.使用内置默认线程池+thenRun执行任务
private static void test1() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException {
CompletableFuture<Void> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->{
try {Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
System.out.println("1号任务"+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "abcd";
}).thenRun(() ->{
try {Thread.sleep(200);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
System.out.println("2号任务"+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).thenRun(() -> {
try {Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
System.out.println("3号任务"+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).thenRun(() -> {
try {Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
System.out.println("4号任务"+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
System.out.println(completableFuture.get(2L,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println("===============");
}
//b.使用自定义线程池+thenRun执行任务
private static void test2() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
CompletableFuture<Void> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->{
try {Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
System.out.println("1号任务"+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "abcd";
},executorService).thenRun(() ->{
try {Thread.sleep(200);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
System.out.println("2号任务"+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).thenRun(() -> {
try {Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
System.out.println("3号任务"+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).thenRun(() -> {
try {Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
System.out.println("4号任务"+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
System.out.println(completableFuture.get(2L,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
executorService.shutdown();
System.out.println("===============");
}
//c.使用内置默认线程池+thenRunAsync执行任务
private static void test3() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException {
CompletableFuture<Void> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->{
try {Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
System.out.println("1号任务"+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "abcd";
}).thenRunAsync(() ->{
try {Thread.sleep(200);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
System.out.println("2号任务"+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).thenRun(() -> {
try {Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
System.out.println("3号任务"+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).thenRun(() -> {
try {Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
System.out.println("4号任务"+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
System.out.println(completableFuture.get(2L,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println("===============");
}
//d.使用自定义线程池+thenRunAsync执行任务
private static void test4() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4);
CompletableFuture<Void> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->{
try {Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
System.out.println("1号任务"+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "abcd";
},executorService).thenRunAsync(() ->{
try {Thread.sleep(200);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
System.out.println("2号任务"+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).thenRun(() -> {
try {Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
System.out.println("3号任务"+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).thenRun(() -> {
try {Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
System.out.println("4号任务"+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
System.out.println(completableFuture.get(2L,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
executorService.shutdown();
System.out.println("===============");
}
//e.模拟任务执行速度快的情况,系统底层会使用main线程处理任务
private static void test0() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException {
CompletableFuture<Void> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->{
System.out.println("1号任务"+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "abcd";
}).thenRun(() ->{
System.out.println("2号任务"+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).thenRun(() -> {
System.out.println("3号任务"+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).thenRun(() -> {
System.out.println("4号任务"+"\t"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
System.out.println(completableFuture.get(2L,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println("===============");
}
}线程池运行选择总结
1)没有传入自定义线程池时,都使用默认线程池ForkJoinPool;
2)执行第一个任务时传入了一个自定义线程池 则当使用thenRun执行之后的任务时,都共用同一个自定义线程池;
3)执行第一个任务时传入了一个自定义线程池 则当使用thenRunAsync执行之后的任务时,只有第一个任务使用的自定义线程池,后续任务都使用的是默认ForkJoin线程池;
4)有可能处理太快的时候,由于系统底层优化原则,直接利用main线程处理任务。
5)其它如thenAccept、thenAcceptAsync、thenApply和thenApplyAsync等,它们之间的区别也同理。
五、应用场景
先A后B的场景应用
package com.gyd;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class CompletableFutureDemo2 {
//先A后B的场景应用
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//推荐配置自定义的线程池!!
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
try {
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//第一步
int result = new Random().nextInt(10);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 出结果:" + result);
return result;
},executorService).whenComplete((v, e) -> {
//第二步,获取第一步的结果
if (null == e) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 接收到结果:" + v);
}
}).exceptionally(e -> {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("发生异常了:" + e);
return null;
});
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"主线程去忙别的事情");
//主线程不要立刻结束,否则CompletableFuture默认使用的线程池会立刻关闭,这里暂停3秒钟
try{ Thread.sleep(3000);}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
}并发执行并获取汇总结果的场景应用
package com.gyd;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class CompletableFutureDemo3 {
static List<NetMall> list = Arrays.asList(
new NetMall("jd"),
new NetMall("dangdang"),
new NetMall("taobao"));
//串行版本
public static List<String> getPrice(List<NetMall> list,String productName) {
return list.stream()
.map(netMall ->
String.format(productName+" in %s price is %.2f",
netMall.getNetMallName(),
netMall.calPrice(productName)))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
//并行版本
public static List<String> getPriceByCompletableFuture(List<NetMall> list,String productName) {
return list.stream().map(netMall -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->
String.format(productName+"in %s price is %.2f",netMall.getNetMallName(),netMall.calPrice(productName))))
.collect(Collectors.toList())
.stream()
.map(s -> s.join())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
List<String> list1 = getPrice(list,"mysql");
for (String element : list1) {
System.out.println(element);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis()-startTime;
System.out.println("costTime:"+endTime);
System.out.println("=======================");
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
List<String> list2 = getPriceByCompletableFuture(list,"mysql");
for (String element : list2) {
System.out.println(element);
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis()-startTime;
System.out.println("======costTime2 "+endTime);
}
}
class NetMall {
String netMallName;
public String getNetMallName() {
return netMallName;
}
public NetMall(String netMallName){this.netMallName = netMallName;}
public Double calPrice(String productName){
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextDouble()*2+productName.charAt(0);
}
}