JAVA中的IO编程框架入门
IO编程学习笔记
一、什么是IO流
I : Input 代表输入 O : Output 代表输出
通过IO可以完成硬盘文件的读和写。 
二、IO流的分类
IO流分为四大类:输入流、输出流、字节流、字符流。
1)以内存作为参照物,按照 流的方向 进行分类:
往内存中去:叫做输入(Input)。或者叫做读(Read)。 从内存中出来:叫做输出(Output)。或者叫做写(Write)。
2)按照 读取数据方式 不同进行分类:
- 按照 字节 的方式读取数据,一次读取1个字节byte,等同于一次读取8个二进制位。 这种流是万能的,什么类型的文件都可以读取。包括:文本文件,图片,声音文件,视频文件 等…
示例
假设文件file1.txt中的内容是"a中国bc张三fe",采用字节流的话是这样读的:
第一次读:一个字节,正好读到’a’ 第二次读:一个字节,正好读到’中’字符的一半。 第三次读:一个字节,正好读到’中’字符的另外一半。
- 按照 字符 的方式读取数据的,一次读取一个字符. 这种流是为了方便读取 普通文本文件 而存在的,这种流不能读取:图片、声音、视频等文件。只能读取 纯文本文件,连word文件都无法读取。
注意:纯文本文件,不单单是.txt文件,还包括 .java、.ini、.py 。总之只要 能用记事本打开 的文件都是普通文本文件。
示例
假设文件file1.txt中的内容是"a中国bc张三fe",采用字符流的话是这样读的:
第一次读:'a’字符('a’字符在windows系统中占用1个字节。)
第二次读:'中’字符('中’字符在windows系统中占用2个字节。)
三、常用API
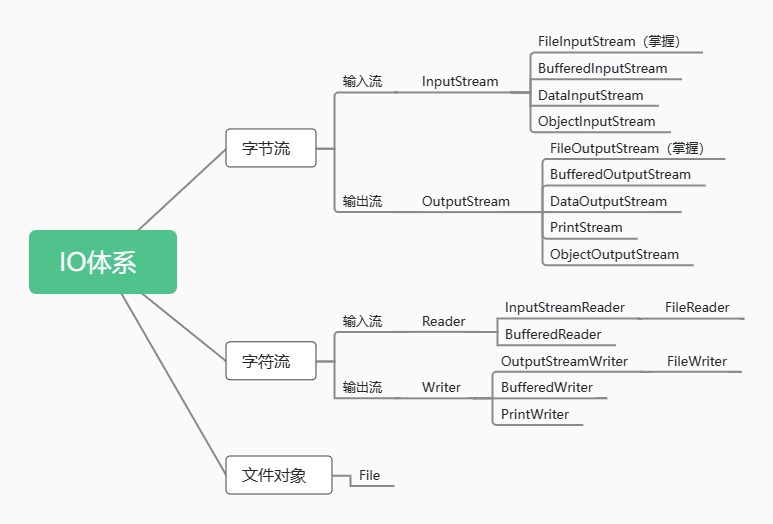
IO编程框架的顶层设计是四个抽象类,分别如下:
- 字节流
//字节输入流
java.io.InputStream
//字节输出流
java.io.OutputStream- 字符流
//字符输入流
java.io.Reader
//字符输出流
java.io.WriterIO框架里所有的流都实现了:java.io.Closeable接口,都是可关闭的,都有 close() 方法。IO流是一个管道,这个是内存和硬盘之间的通道,用完之后一定要调用close关闭,不然会耗费(占用)很多资源。
IO框架所有的 输出流 都实现了:java.io.Flushable接口,都是可刷新的,都有 flush() 方法。 养成一个好习惯,输出流在最终输出之后,一定要记得flush()刷新一下。这个刷新表示将通道/管道当中剩余未输出的数据强行输出完(清空管道!)刷新的作用就是清空管道。
在JAVA的IO编程框架里,只要“类名”以 Stream 结尾的都是字节流,以“ Reader/Writer ”结尾的都是字符流。
Java要掌握的流主要有16个:
- 文件操作
java.io.FileInputStream
java.io.FileOutputStream
java.io.FileReader
java.io.FileWriter- 转换流:(将字节流转换成字符流)
java.io.InputStreamReader
java.io.OutputStreamWriter- 缓冲流:
java.io.BufferedReader
java.io.BufferedWriter
java.io.BufferedInputStream
java.io.BufferedOutputStream- 数据流:
java.io.DataInputStream
java.io.DataOutputStream- 标准输出流
java.io.PrintWriter
java.io.PrintStream(掌握)- 对象流:
java.io.ObjectInputStream(掌握)
java.io.ObjectOutputStream(掌握)File文件类
java.io.File1、FileInputStream
文件字节输入流,万能的,任何类型的文件都可以采用这个流来读
构造方法:
| 构造方法名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| FileInputStream(String name) | name为文件路径 |
| FileInputStream(File file) | file文件类对象 |
常用方法:
| 方法名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| int read() | 读取一个字节,返回值为该字节ASCII码;读到文件末尾返回-1 |
| int read(byte[] b) | 读b数组长度的字节到b数组中,返回值为读到的字节个数;读到文件末尾返回-1 |
| int read(byte[] b, int off, int len) | 从b素组off位置读len长度的字节到b数组中,返回值为读到的字节个数;读到文件末尾返回-1 |
| int available() | 返回文件有效的字节数 |
| long skip(long n) | 跳过n个字节 |
| void close() | 关闭文件输入流 |
2、FileOutputStream
构造方法
| 构造方法名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| FileOutputStream(String name) | name为文件路径 |
| FileOutputStream(String name, boolean append) | name为文件路径,append为true表示在文件末尾追加;为false表示清空文件内容,重新写入 |
| FileOutputStream(File file) | file为文件类对象 |
| FileOutputStream(File file, boolean append) | file为文件类对象,append为true表示在文件末尾追加;为false表示清空文件内容,重新写入 |
常用方法:
| 方法名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| void write(int b) | 将指定字节写入文件中 |
| void write(byte[] b) | 将b.length个字节写入文件中 |
| void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) | 将b素组off位置开始,len长度的字节写入文件中 |
| void flush() | 刷新此输出流并强制写出所有缓冲的输出字节 |
| void close() | 关闭文件输出流 |
3、FileReader
构造方法:
| 构造方法名 | 备注 |
|---|---|
| FileReader(String fileName) | name为文件路径 |
| FileReader(File file) |
常用方法:
| 方法名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| int read() | 读取一个字符,返回值为该字符ASCII码;读到文件末尾返回-1 |
| int read(char[] c) | 读c数组长度的字节到c数组中,返回值为读到的字符个数;读到文件末尾返回-1 |
| int read(char[] c, int off, int len) | 从c素组off位置读len长度的字符到c数组中,返回值为读到的字符个数;读到文件末尾返回-1 |
| long skip(long n) | 跳过n个字符 |
| void close() | 关闭文件输入流 |
4、FileWriter
FileWriter文件字符输出流。写。只能输出普通文本。
| 构造方法名 | 备注 |
|---|---|
| FileWriter(String fileName) | name为文件路径 |
| FileWriter(String fileName, boolean append) | name为文件路径,append为true表示在文件末尾追加;为false表示清空文件内容,重新写入 |
| FileWriter(File file) | |
| FileWriter(File file, boolean append) | append为true表示在文件末尾追加;为false表示清空文件内容,重新写入 |
5、BufferedReader、InputStreamReader
BufferedReader是带有缓冲区的字符输入流。使用这个流的时候不需要自定义char数组,或者说不需要自定义byte数组。自带缓冲。
InputStreamReader是字节输入流转字符输入流
构造方法:
| 构造方法名 | 备注 |
|---|---|
| BufferedReader(Reader in) | in为reader对象(可以是reader的实现类) |
常用方法:
| 方法名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| int read() | 读取一个字符,返回值为该字符ASCII码;读到文件末尾返回-1 |
| int read(char[] c) | 读c数组长度的字节到c数组中,返回值为读到的字符个数;读到文件末尾返回-1 |
| String readLine() | 读取文件一行 |
| long skip(long n) | 跳过n个字符 |
| void close() | 关闭文件输入流 |
6、BufferedWriter、 OutputStreamWriter
BufferedWriter:带有缓冲的字符输出流。 OutputStreamWriter:字节输出流转字符输出流
构造方法:
| 构造方法名 | 备注 |
|---|---|
| BufferedWriter(Writer out) | out为Writer对象(可以是reader的实现类) |
常用方法:
| 方法名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| void write(int c) | 将指定字符写入文件中 |
| void write(char[] c, int off, int len) | 将c素组off位置开始,len长度的字符写入文件中 |
| void write(String str, int off, int len) | 从字符串off位置开始截取len长度的字符串写入文件 |
| void flush() | 刷新此输出流并强制写出所有缓冲的输出字符 |
| void close() | 关闭文件输出流 |
7、DataInputStream
DataInputStream:数据字节输入流。
DataOutputStream写的文件,只能使用DataInputStream去读。并且读的时候你需要提前知道写入的顺序。
读的顺序需要和写的顺序一致。才可以正常取出数据。 构造方法:
| 构造方法名 | 备注 |
|---|---|
| DataInputStream(InputStream in) | in为InputStream对象 |
常用方法:
| 方法名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| boolean readBoolean() | 从文件中读取boolean字节数据 |
| byte readByte() | 从文件中读取byte字节数据 |
| char readChar() | 从文件中读取char字节数据 |
| double readDouble() | 从文件中读取double字节数据 |
| float readFloat() | 从文件中读取float字节数据 |
| int readInt() | 从文件中读取int字节数据 |
| long readLong() | 从文件中读取long字节数据 |
| short readShort() | 从文件中读取short字节数据 |
8、DataOutputStream
java.io.DataOutputStream:数据字节输出流。
这个流可以将 数据连同数据的类型 一并写入文件。
注意:这个文件不是普通文本文档。(这个文件使用记事本打不开。)
构造方法:
| 构造方法名 | 备注 |
|---|---|
| DataOutputStream(OutputStream out) | out为OutputStream 对象 |
常用方法:
| 方法名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| void writeBoolean(boolean v) | 将boolean字节写入文件 |
| void writeByte(int v) | 将byte字节写入文件 |
| void writeBytes(String s) | 将bytes字节(字符串)写入文件 |
| void writeChar(int v) | 将char字节写入文件 |
| void writeChars(String s) | 将chars字节(字符串)写入文件 |
| void writeDouble(double v) | 将double字节写入文件 |
| void writeFloat(float v) | 将float字节写入文件 |
| void writeInt(int v) | 将int字节写入文件 |
| void writeLong(long v) | 将long字节写入文件 |
| void writeShort(int v) | 将short字节写入文件 |
| void flush() | 刷新此输出流并强制写出所有缓冲的输出字符 |
9、PrintStream
java.io.PrintStream:标准的字节输出流。默认输出到控制台。
构造方法:
| 构造方法名 | 备注 |
|---|---|
| PrintStream(File file) | |
| PrintStream(OutputStream out) | |
| PrintStream(String fileName) | fileName文件地址 |
常用方法:
| 方法 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| println(参数类型不定 x) | 输出x带换行 |
| print(参数类型不定 x) | 输出x不带换行 |
| void flush() | 刷新此输出流并强制写出所有缓冲的输出字符 |
| void close() | 关闭流 |
10、ObjectOutputStream
ObjectInputStream:反序列化对象
11、ObjectInputStream
ObjectInputStream:反序列化对象
12、File
File对象代表文件 和 目录路径名 的抽象表示形式。
C:\Drivers 这是一个File对象
C:\Drivers\Lan\Realtek\Readme.txt 也是File对象。
一个File对象有可能对应的是目录,也可能是文件。
File只是一个 路径名 的抽象表示形式。构造方法:
| 构造方法名 | 备注 |
|---|---|
| File(String pathname) | pathname文件/文件夹路径 |
常用方法:
| 方法名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| boolean delete() | 删除文件/文件夹 |
| boolean exists() | 判断文件/文件夹是否存在 |
| -------- | -------- |
| File getAbsoluteFile() | 获取文件/文件夹的绝对路径(返回值:File) |
| String getName() | 获得文件/文件夹名字 |
| String getParent() | 获取文件/文件夹的父文件/文件夹 |
| File getParentFile() | 获取文件/文件夹的父文件/文件夹(返回值:File) |
| String getPath() | 获取文件/文件夹的路径 |
| boolean isDirectory() | 判断该文件/文件夹是不是文件夹 |
| isFile() | 判断该文件/文件夹是不是文件 |
| isHidden() | 判断该文件/文件夹是否隐藏 |
| -------- | -------- |
| long lastModified() | 获取文件/文件夹最后一次修改时间 |
| long length() | 获取文件大小;获取文件夹里面的文件个数 |
| String[] list() | 获取文件夹的文件名字以String[]返回 |
| File[] listFiles() | 获取文件夹的文件名字以File[]返回 |
| boolean mkdir() | 创建文件/文件夹 |
| boolean mkdirs() | 创建多重文件夹 |
13、测试代码
准备文件test.txt,放在D盘根目录下,文件初始内容如下: 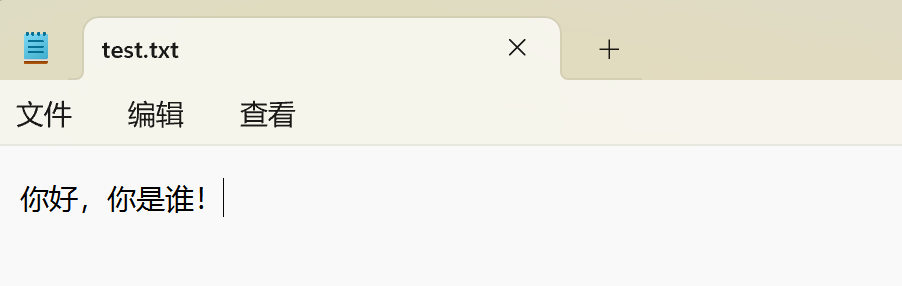
接下来使用各种io类对test.txt文件进行操作演示:
//读取ASCII码打印在控制台上
package com.gyd.io;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
class FileInputStreamTest01{
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\test.txt");
int res = fis.read();//读到返回该字符ASCII码,没读到返回-1
System.out.println(res);
res = fis.read();
System.out.println(res);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fis != null) {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}//读取实际中文展示在控制台上
package com.gyd.io;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
public class FileInputStreamTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\test.txt");
byte[] b = new byte[30];//读中文时,数据需开大一点,否则会乱码(一个汉字等于两字节)
int readCount = 0;
while((readCount = fis.read(b)) != -1){
System.out.println(new String(b, 0, readCount));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fis != null) {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}//读取实际中文展示在控制台上
package com.gyd.io;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
public class FileInputStreamTest03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\test.txt");
byte[] b = new byte[fis.available()];//不适合大数据量,因为内存中很难找到一块连续的空间
fis.read(b);//一次读完
System.out.println(new String(b));//你好,你是谁!
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fis != null) {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}//按字节写入文件内容,文件内容最终是:"ABCDabcdbc"
class FileOutputStreamTest01{
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\test.txt");//没有文件会自动创建,每次自动清空文件内容,慎用!!!
fos.write(65);//字符的ASCII码
fos.write(66);
fos.write(67);
fos.write(68);
byte[] b = {97, 98, 99 , 100};
fos.write(b);
fos.write(b, 1, 2);
fos.flush();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fos != null) {
try {
fos.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}class FileOutputStreamTest02{
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\test.txt", true);
byte[] b = {97, 98, 99 , 100};
fos.write(b, 2, 1);
String s = "你好你好,大家好";
byte[] bytes = s.getBytes();
fos.write(bytes);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fos != null) {
try {
fos.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}//文件复制
package com.gyd.io;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
public class FileCopy01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\test.txt");
fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\test-copy.txt");
byte[] b = new byte[1024 * 1024];//1MB
int readCount = 0;
//一边读一边写
while ((readCount = fis.read(b)) != -1){
fos.write(b, 0 , readCount);
}
fos.flush();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fos != null) {
try {
fos.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (fis != null) {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}//使用FileReader进行文件读取
package com.gyd.io;
import java.io.FileReader;
public class FileReaderTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileReader in = null;
try {
in = new FileReader("D:\\test.txt");
int readCount = 0;
while ((readCount = in.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char)readCount);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (in != null) {
try {
in.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}package com.gyd.io;
import java.io.FileReader;
public class FileReaderTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileReader reader = null;
try {
reader = new FileReader("D:\\test.txt");
char[] c = new char[4];
int readCount = 0;
while ((readCount = reader.read(c)) != -1){
System.out.println(new String(c, 0, readCount));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (reader != null) {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}//使用FileWriter进行文件写入
package com.gyd.io;
import java.io.FileWriter;
public class FileWriterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileWriter writer = null;
try {
writer = new FileWriter("D:\\test.txt", true);
writer.write(87);
writer.write("你是中国人,中国人很好");
char[] c = {'\n', '你', '好', '中', '国'};
writer.write(c);
writer.write(c, 1, 2);
writer.flush();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (writer != null) {
try {
writer.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}//FileReader文件复制
package com.gyd.io;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
public class FileCopy02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileReader reader = null;
FileWriter writer = null;
try {
reader = new FileReader("D:\\test.txt");
writer = new FileWriter("D:\\test-new.txt");
char[] c = new char[1024 * 512];//1MB
int readCount = 0;
//边读边写
while((readCount = reader.read(c)) != -1){
writer.write(c, 0, readCount);
}
writer.flush();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
if (writer != null) {
try {
writer.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (reader != null) {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}//BufferedReader文件读取
package com.gyd.io;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
public class BufferedReaderTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader reader = null;
try {
FileReader fr = new FileReader("D:\\test.txt");//节点流
reader = new BufferedReader(fr);//包装流
int readCount = 0;
while ((readCount = reader.read()) != -1){//单个取
System.out.print((char)readCount);//加ln排版有问题
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
if (reader != null) {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}//BufferedReader文件读取
package com.gyd.io;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
public class BufferedReaderTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader reader = null;
try {
reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("D:\\test.txt"));
int readCount = 0;
char[] c = new char[10];//字节数组
while ((readCount = reader.read(c)) != -1){
System.out.print(new String(c, 0, readCount));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
if (reader != null) {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}class BufferedReaderTest03{
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader reader = null;
try {
reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("D:\\test.txt"));
String res = "";
while((res = reader.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(res);//readLine()读不到换行符,需要手动换行
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
if (reader != null) {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}//BufferWriter文件写入
package com.gyd.io;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
public class BufferWriter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedWriter writer = null;
try {
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("D:\\test.txt", true);
writer = new BufferedWriter(fw);
writer.write(97);
writer.write("中国人世界第一");
writer.write(new char[]{'中', '国', '人'});
writer.flush();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if (writer != null) {
try {
writer.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}package com.gyd.io;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class BufferedReaderTest04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader reader = null;
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\test.txt");
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);//字节流转字符流
reader = new BufferedReader(isr);
String res = "";
while((res = reader.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(res);//readLine()读不到换行符,需要手动换行
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
if (reader != null) {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}//DataOutputStream写入文件(会乱码)
package com.gyd.io;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
public class DataOutputStream01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DataOutputStream dos = null;
try {
dos = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\test.txt", true));
byte b = 1;
short s = 2;
int i = 3;
long l = 4L;
float f = 3.99F;
double d = 3.14;
boolean flag = true;
char sex = '男';
dos.writeByte(b);
dos.writeShort(s);
dos.writeInt(i);
dos.writeLong(l);
dos.writeFloat(f);
dos.writeDouble(d);
dos.writeBoolean(flag);
dos.writeChar(sex);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
if (dos != null) {
try {
dos.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}//DataInputStream文件读取
package com.gyd.io;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
public class DataInputStreamTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DataInputStream dis = null;
try {
dis = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\\test.txt"));
System.out.println(dis.readByte());
System.out.println(dis.readShort());
System.out.println(dis.readInt());
System.out.println(dis.readLong());
System.out.println(dis.readFloat());
System.out.println(dis.readDouble());
System.out.println(dis.readBoolean());
System.out.println(dis.readChar());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (dis != null) {
try {
dis.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}//PrintStream输出到文件
package com.gyd.io;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.PrintStream;
public class PrintStreamTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//1.改变流的输出方向
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\test.txt", true));
//PrintStream ps = new PrintStream("D:/IO/writer7.txt");//会清空内容
System.setOut(ps);
System.out.println("hello world");
System.out.println("你好世界");
System.out.println("hi world");
//标准输出流不需要关闭
//ps.flush();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}//File操作文件
package com.gyd.io;
import java.io.File;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @ClassName FileTest01
* @Description TODO
* @Author guoyading
* @Date 2023/8/8 16:02
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class FileTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f1 = new File("D:\\test1");
if (!f1.exists()){
try {
f1.createNewFile();//创建文件
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
File f2 = new File("D:\\test2");
if (!f2.exists()){
f2.mkdir();//创建文件夹
}
File f3 = new File("D:\\a/b/c/d/e/f/g/h/i");
if (!f3.exists()){
f3.mkdirs();//创建多重文件夹
}
File f5 = new File("D:\\felete");
f5.delete();
File f4 = new File("D:\\新建文件夹");
String s1 = f4.getName();//新建文件夹
System.out.println(s1);
String s2 = f4.getParent();
System.out.println(s2);
String s3 = f4.getPath();//D:\\新建文件夹
System.out.println(s3);
String s4 = f4.getAbsolutePath();//D:\\新建文件夹
System.out.println(s4);
File asf = f4.getAbsoluteFile();
System.out.println(asf.getAbsolutePath());//D:\\新建文件夹
File pf = f4.getParentFile();
System.out.println(pf.getAbsolutePath());//D:
System.out.println(f4.isDirectory());//true
System.out.println(f4.isFile());//false
System.out.println(f4.isHidden());//false
System.out.println(f4.isAbsolute());//true
File f6 = new File("D:\\test.txt");
System.out.println(f6.length());//5743字节
long lastModify = f6.lastModified();//最后修改时间
Date d = new Date(lastModify);
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String date = sdf.format(d);
System.out.println(date);//2021-05-03 22:55:06
File f7 = new File("D:\\a");
String[] strList = f7.list();
for (String s : strList){
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
File[] fileList = f7.listFiles();
for (File f : fileList){
//System.out.println(f.getPath());
System.out.println(f.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
}//可序列化的对象定义
package com.gyd.io;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Objects;
class MyObject implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private int age;
private String name;
private transient float weight;//不参与序列化,反序列化出来为默认值
public MyObject() {
}
public MyObject(int age, String name, float weight) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
this.weight = weight;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyObject{" +
"age=" + age +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", weight=" + weight +
'}';
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
MyObject that = (MyObject) o;
return age == that.age &&
Objects.equals(name, that.name);
}
}//ObjectOutputStream将对象写入文件(对象需要支持序列化)
package com.gyd.io;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
public class ObjectOutputStreamTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
try {
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\test.txt"));
MyObject a = new MyObject(18, "a", 150.0F);
MyObject b = new MyObject(18, "b", 123F);
oos.writeObject(a);
oos.writeObject(b);
oos.flush();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
if (oos != null) {
try {
oos.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}package com.gyd.io;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class ObjectOutputStreamTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
try {
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\test.txt"));
List<MyObject> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new MyObject(18, "a", 190));
list.add(new MyObject(18, "b", 155));
list.add(new MyObject(18, "c", 132));
list.add(new MyObject(18, "d", 112));
oos.writeObject(list);
oos.flush();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
if (oos != null) {
try {
oos.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}//ObjectInputStream读取文件中的对象
package com.gyd.io;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
public class ObjectInputStreamTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try {
ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\\test.txt"));
Object o = ois.readObject();
if (o instanceof MyObject){
MyObject a = (MyObject) o;
System.out.println(a);
}
o = ois.readObject();
if (o instanceof MyObject){
MyObject a = (MyObject) o;
System.out.println(a);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
if (ois != null) {
try {
ois.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}package com.gyd.io;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class ObjectInputStreamTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try {
ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\\test.txt"));
Object o = ois.readObject();
if (o instanceof List){
ArrayList list = (ArrayList) o;
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++){
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
if (ois != null) {
try {
ois.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}四、参考资料
站在前人的肩膀上学习知识!