性能测试工具-JMeter入门
性能测试工具-JMeter入门
一、前言
性能测试(压测)是企业项目必须要做的一个环节,下面总结在性能测试中常用的工具JMeter的简单使用。
二、安装
官方下载链接:https://jmeter.apache.org/download_jmeter.cgi 
三、配置和启动
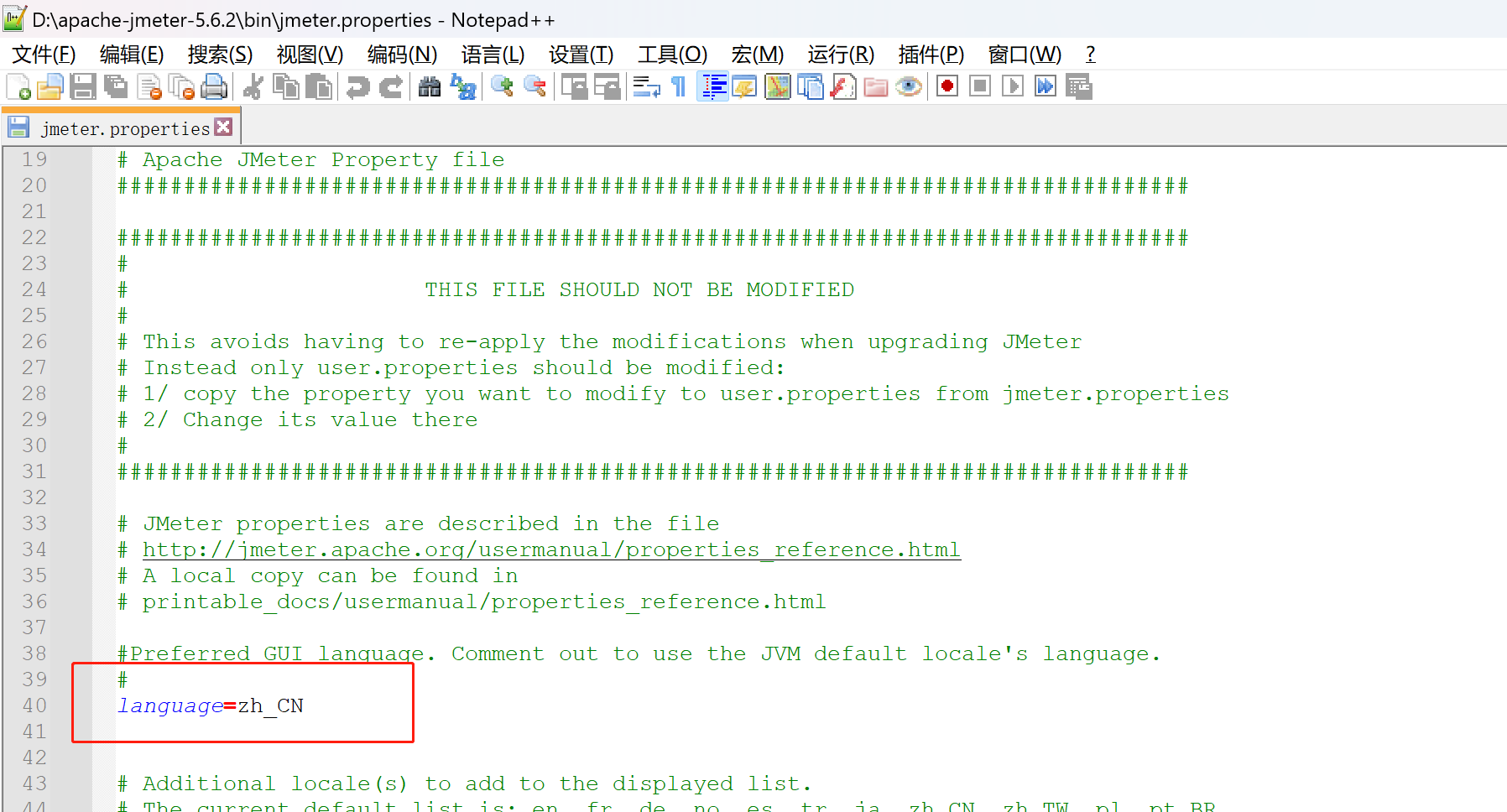
配置:解压下载好的程序zip包,并找到文件 jmeter.properties 修改语言 [optional]
启动:进入bin目录,并双击jmeter.bat运行,需要等一会,并且本机需要提前准备好Java环境
此时会弹出两个界面,一个是命令窗口,一个是图形化窗口,意味着JMeter已经安装和运行成功了。
命令窗口: 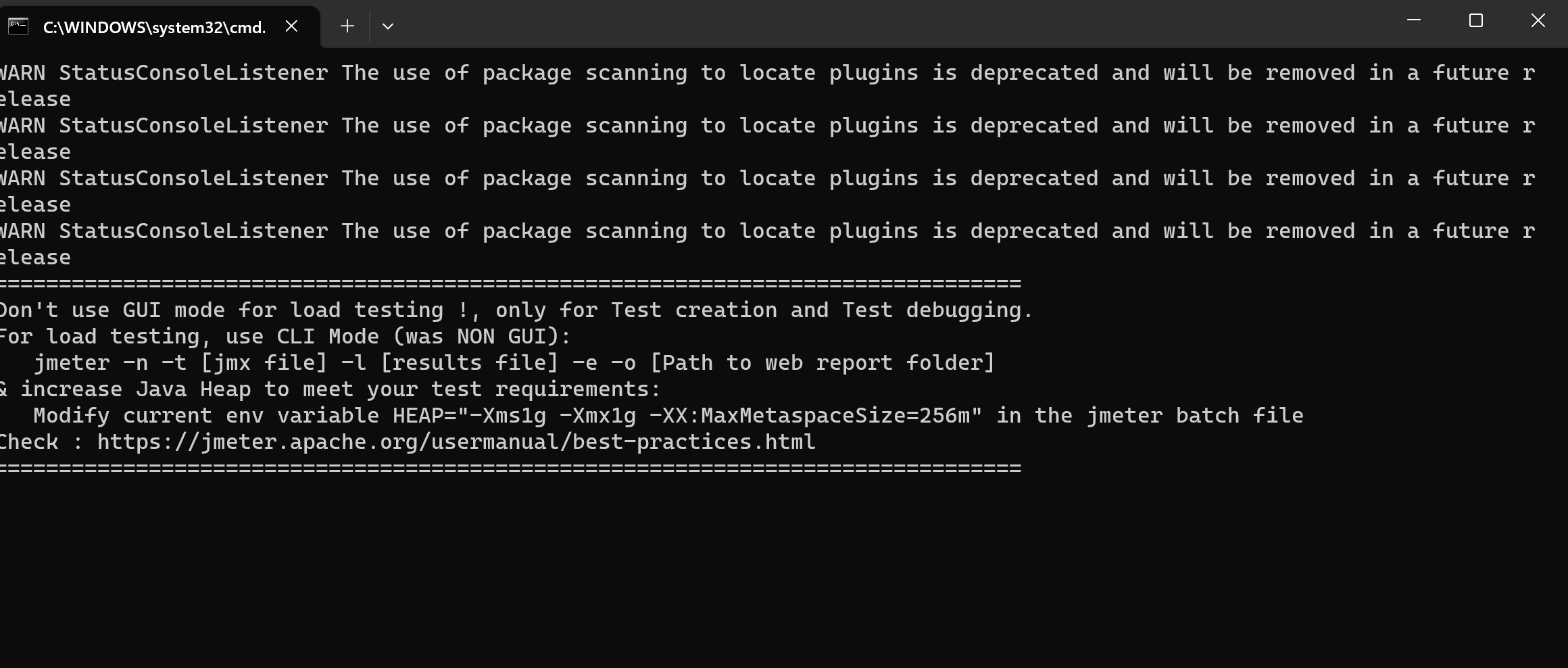
图形化窗口: 
四、简单使用
下面用一个接口压测场景来演示JMeter的简单使用。
接口业务场景:对数据库同一条记录进行并发更新,主要统计当天进和出的人流量。
1、业务表结构
CREATE TABLE `demo` (
`id` int unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`cur_date` varchar(20) COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '当前日期',
`up` bigint unsigned DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '出',
`down` bigint unsigned DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '进',
`insert_time` timestamp NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '插入时间',
`update_time` timestamp NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '更新时间',
`operator` varchar(100) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '操作人',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `ai_people_stat_UN` (`cur_date`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=7 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_general_ci COMMENT='人员进出统计';2、业务接口逻辑代码
package com.gyd.service.impl;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.query.QueryWrapper;
import com.gyd.AiPeopleStatDto;
import com.gyd.AiPeopleStatRequestDto;
import com.gyd.entity.AiPeopleStatEntity;
import com.gyd.mapper.AiPeopleStatMapper;
import com.gyd.service.DemoService;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
/**
* 业务处理类
*/
@Service
public class DemoServiceImpl implements DemoService {
@Resource
private DemoMapper mapper;
@Override
public AiPeopleStatDto save(AiPeopleStatRequestDto request){
String curDate = DateUtils.getCurrentDay();
AiPeopleStatDto result = new AiPeopleStatDto();
//对吞吐量有影响
QueryWrapper<AiPeopleStatEntity> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.eq("cur_date",curDate);
AiPeopleStatEntity entity = mapper.selectOne(wrapper);
if (null == entity) {
entity = new AiPeopleStatEntity();
entity.setInsertTime(DateUtils.getCurrentDate());
entity.setCurDate(curDate);
entity.setUp(0L);
entity.setDown(0L);
}
entity.setOperator(StringUtils.isNoneBlank(request.getOperator()) ? request.getOperator() : "admin");
entity.setUpdateTime(DateUtils.getCurrentDate());
entity.setUp(entity.getUp()+request.getUp());
entity.setDown(entity.getDown()+request.getDown());
mapper.insertOrUpdate(entity);
BeanUtils.copyProperties(entity,result);
return result;
}
}package com.gyd.service.impl;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.query.QueryWrapper;
import com.gyd.dto.AiPeopleStatDto;
import com.gyd.dto.AiPeopleStatRequestDto;
import com.gyd.entity.AiPeopleStatEntity;
import com.gyd.mapper.AiPeopleStatMapper;
import com.gyd.service.AiPeopleStatLockService;
import com.gyd.service.AiPeopleStatService;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Service
public class DemoLockServiceImpl implements DemoLockService {
@Resource
private DemoService service;
@Override
public AiPeopleStatDto save(AiPeopleStatRequestDto request){
if (request.getUp() == null && request.getDown() == null) {
throw new RunTimeException("提交参数有误,请检查");
}
AiPeopleStatDto result;
//对吞吐量有影响
//因为默认开启了事务,直接在事务控制的方法里加synchronized是不生效的。需要在事务调用前开启synchronized
synchronized (this) {
result = service.save(request);
}
return result;
}
}接口访问入口代码如下:
package com.gyd.controller;
import com.gyd.dto.AiPeopleStatDto;
import com.gyd.dto.AiPeopleStatRequestDto;
import com.gyd.security.auth.annotation.NoLogin;
import com.gyd.service.AiPeopleStatLockService;
import com.gyd.service.AiPeopleStatService;
import io.swagger.annotations.Api;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("test")
public class DemoController {
@Resource
private DemoStatLockService lockService;
@Resource
private DemoStatService service;
/**
*
* @param request 入参
* @return
*/
@NoLogin
@PostMapping(value = "/stat")
public ResultWrapper<AiPeopleStatDto> stat(@ApiParam @RequestBody AiPeopleStatRequestDto request){
return ResultWrapper.SUCCESS(lockService.stat(request));
}
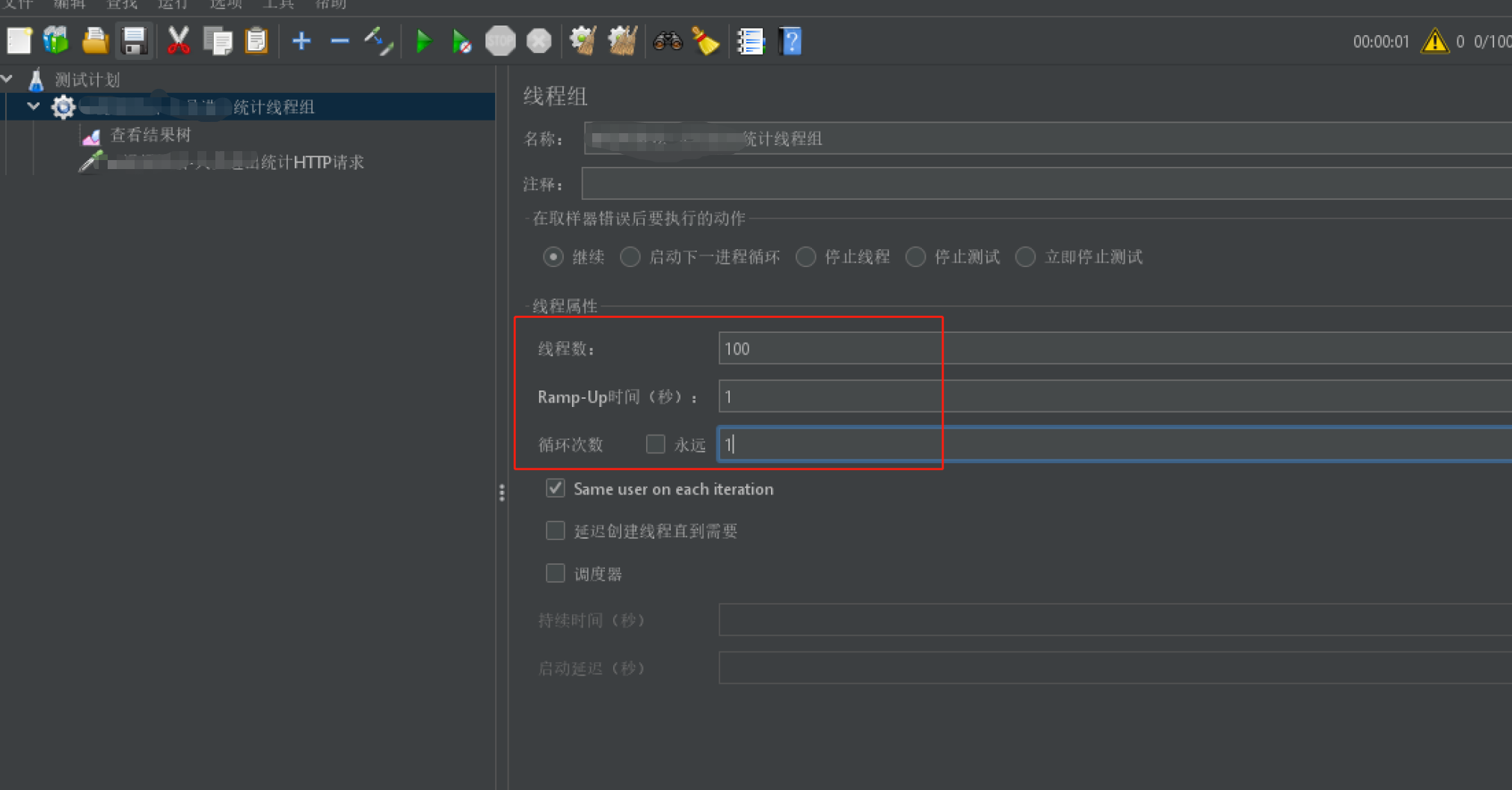
}3、压测参数配置-并发线程和执行次数
计划100个线程并发1次
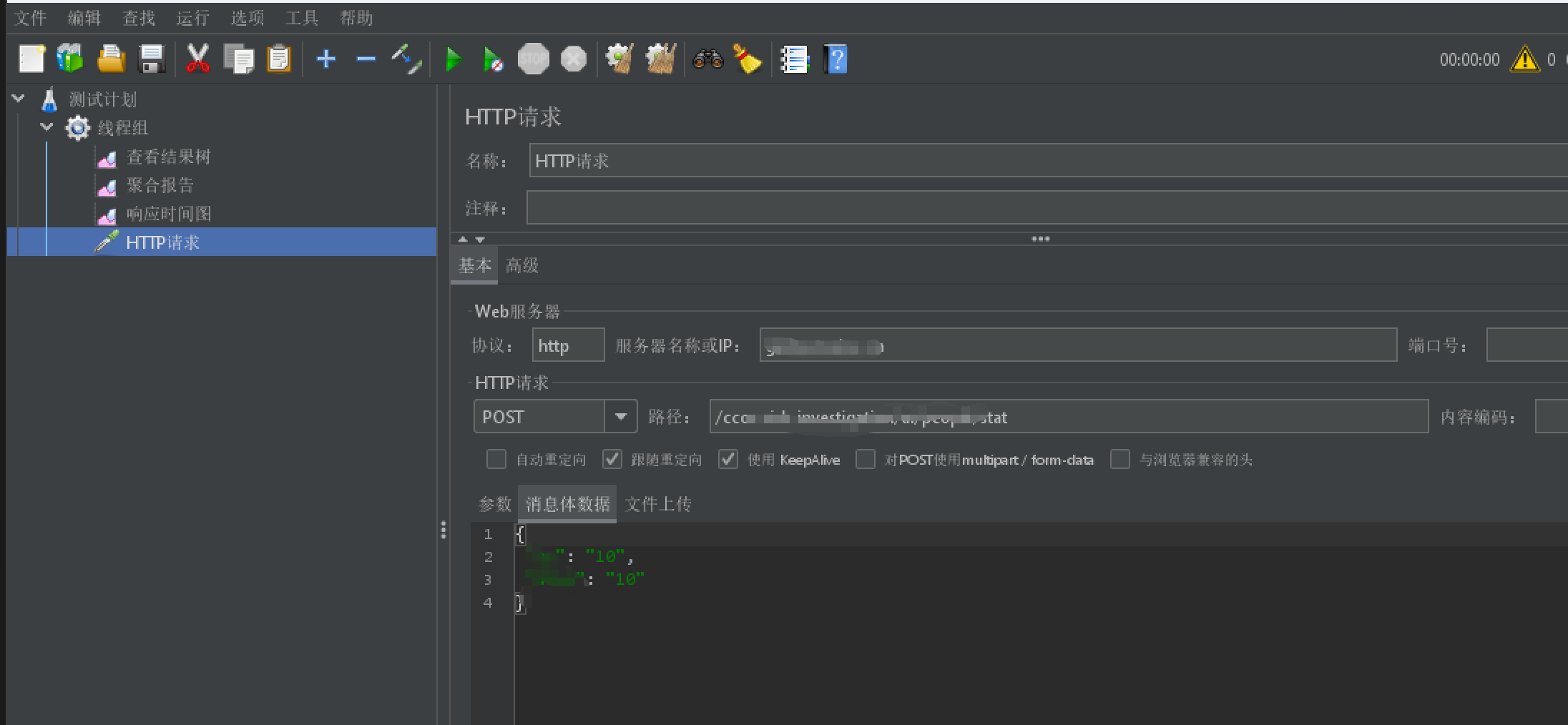
4、压测参数配置-http请求入参配置
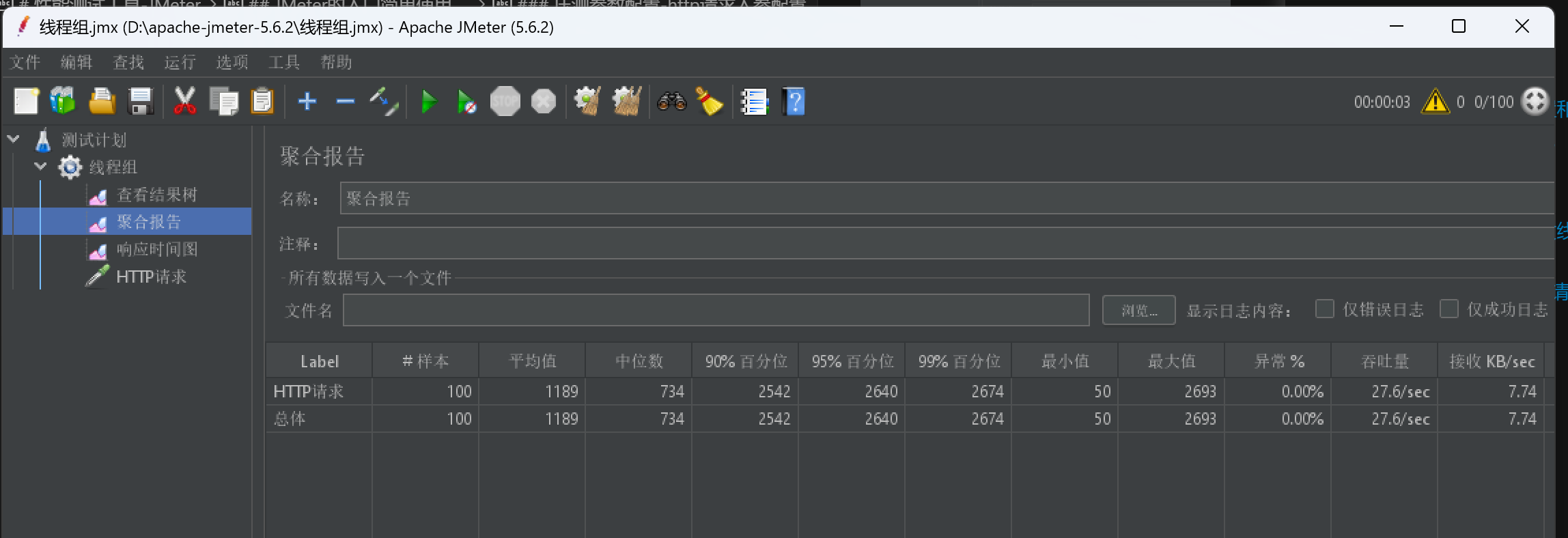
5、压测结果数据查看
选中线程组tab,执行压测

查看结果聚合报告
可以看到各种性能指标数据
对聚合报告的指标解释如下: 1)Label:请求的名称,就是脚本中Sampler的名称。 2)#Samples(样本):总共发给服务器的请求数量,如果模拟10个用户,每个用户迭代10次,那么总的请求数为:10*10 =100次。 3)Average(平均值):默认情况下是单个Request的平均响应时间,当使用了Transaction Controller(事务控制器) 时,也可以用Transaction的时间,来显示平均响应时间 ,单位是毫秒。 4)Median(中位数):50%用户的响应时间小于该值。 5)90% Line(90% 百分位):90%用户的响应时间小于该值。 6)95% Line(95% 百分位):95%用户的响应时间小于该值。 7)99% Line(99% 百分位):99%用户的响应时间小于该值。 8)Min(最小值):最小的响应时间。 9)Maximum(最大值):最大的响应时间。 10)Error%(异常%):错误率=错误请求的数量/请求的总数。 11)Throughput(吞吐量):默认情况下表示每秒完成的请求数(Request per Second)。 12)Received KB/sec (接收数据):每秒从服务器端接收到的数据量。 13)Sent KB/sec(发送):每秒发送到服务器端的数据量。
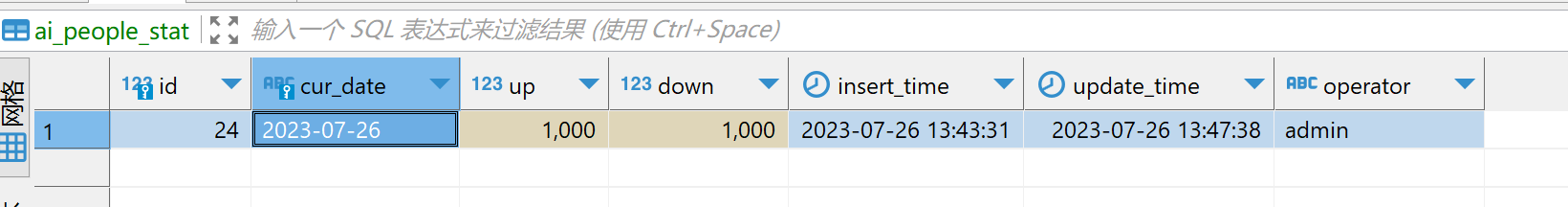
查看数据库最终数据符合预期
6、结论
执行100个线程并发访问1次,预期是1000,数据库符合预期 多次反复执行100个线程访问,数据库均符合预期
并发线程数越高,接口聚合报告中的性能指标数据越差
五、遇到的问题
压测过程遇到一个知识盲区:接口的service方法内增加了synchronized同步代码块机制,但是并发测试并没有生效。排查下来发现这是Spring事务管理下synchronized锁失效问题
原因是:service方法有默认开启事务功能,Spring事务的底层是Spring AOP,而Spring AOP的底层是动态代理技术。
动态代理技术的实现大概是下面这样:
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 目标对象
Object target ;
Proxy.newProxyInstance(ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader(), Main.class, new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// 但凡带有@Transcational注解的方法都会被拦截
// 1... 开启事务
method.invoke(target);
// 2... 提交事务
return null;
}
});
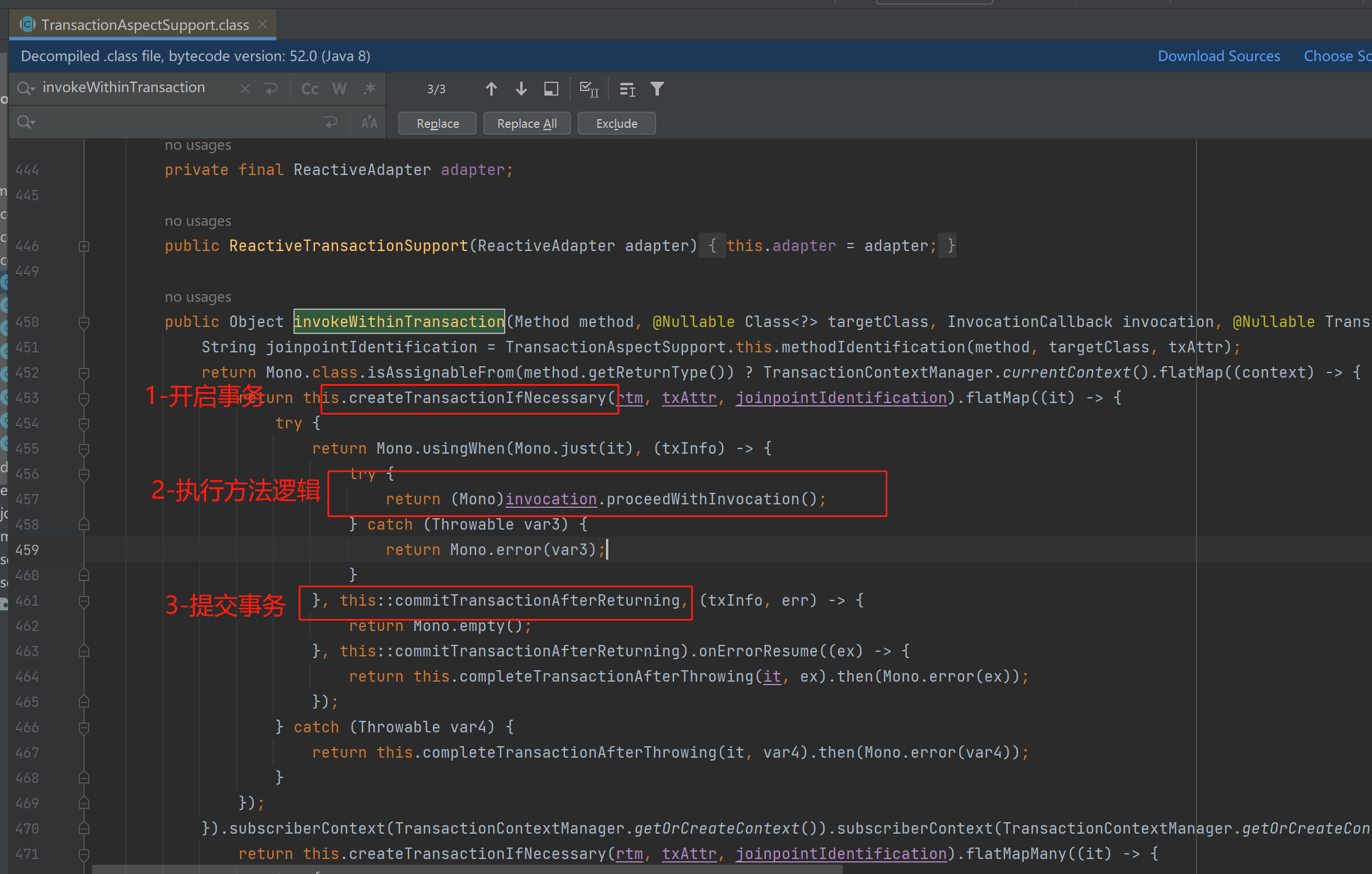
}spring对事务管理的处理流程大概是下面这样:
源码出处:spring-tx包中的TransactionAspectSupport.invokeWithinTransaction方法
看完源码恍然大悟,spring的事务流程是调用service方法前开启事务,调用方法后提交事务,在并发多线程环境下,就可能会出现:方法执行完了(synchronized代码块执行完了),事务还没提交,别的线程可以进入被synchronized修饰的方法,再读取的时候,读到的是还没提交事务的数据,这个数据不是最新的,所以就出现了这个问题。